Back to: Introduction to R
The last tidyr function we will look into is the unite() function. With unite() it will make sense with what we are doing. We will take many columns that share the same type of information and unite them together as 1 column
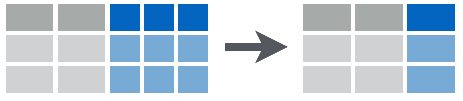
The above picture displays this idea. We can consider table6 :
## # A tibble: 6 × 4
## country century year rate
## <fctr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 Afghanistan 19 99 745/19987071
## 2 Afghanistan 20 00 2666/20595360
## 3 Brazil 19 99 37737/172006362
## 4 Brazil 20 00 80488/174504898
## 5 China 19 99 212258/1272915272
## 6 China 20 00 213766/1280428583It does not make sense to most of us to have a century and year columns but instead to have a 4 digit year. We can use the unite() function to do this:
unite(data,col,..., sep)where
data is the data frame of interest.
col is the column you wish to add.
... is names of columns you wish to unite together.
sep is how you wish to join the data in the columns.
unite() Example
In our example here we would do the following: `
table6 %>%
unite("year", century, year, sep="")## # A tibble: 6 × 3
## country year rate
## * <fctr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 Afghanistan 1999 745/19987071
## 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666/20595360
## 3 Brazil 1999 37737/172006362
## 4 Brazil 2000 80488/174504898
## 5 China 1999 212258/1272915272
## 6 China 2000 213766/1280428583Note that we use quotations around the new column name, but the other two columns century and yearare called in their bare form.
Now we can see that this data is not what we would call tidy yet because the rate column really is not correct. We can fix this with the following code:
table6 %>%
unite("year", century, year, sep="") %>%
separate(rate, c("cases", "population")) %>%
mutate(cases=as.numeric(cases)) %>%
mutate(population=as.numeric(population)) %>%
mutate(rate=cases/population)## # A tibble: 6 × 5
## country year cases population rate
## <fctr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071 0.0000372741
## 2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360 0.0001294466
## 3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362 0.0002193930
## 4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898 0.0004612363
## 5 China 1999 212258 1272915272 0.0001667495
## 6 China 2000 213766 1280428583 0.0001669488We have not learned about the mutate command but it either replaces a value or adds a value. Note that we can do many things in one step with the piping.
On Your Own: Swirl Practice
In order to learn R you must do R. Follow the steps below in your RStudio console:
1. Run this command to pick the course:
swirl()You will be promted to choose a course. Type whatever number is in front of 03 Tidy Data. This will then take you to a menu of lessons. For now we will just use lesson 1. Type 1 to choose Tidying Data with tidyr then follow all the instructions until you are finished.
Once you are finished with the lesson come back to this course and continue.